The physician credentialing process involves a formal evaluation to verify healthcare professionals’ qualifications. The essential procedure verifies that medical professionals achieve the necessary educational standards along with adequate training and expert knowledge. Healthcare organizations and hospitals that follow physician credentialing requirements ensure compliance with standards and protect patients while obtaining proper insurance reimbursements. Successful credentialing in medical billing enables healthcare providers to join an insurer’s network which includes hospitals and other medical facilities. A healthcare operator becomes eligible to receive reimbursements once they complete their application and obtain listed service provider credentials. The reimbursements are received from the insurer.
The healthcare operator receives payments from the insurer for delivering services to the insurer’s enrolled patients. The contractual relationship between an insurer and a healthcare service provider represents a credentialing or contracting agreement. Healthcare facilities achieve top care quality standards while earning patient and insurer trust through comprehensive physician credentialing processes. Credentialing acts as a crucial defense against legal risks while minimizing operational inefficiencies.
Having a structured physician credentialing checklist ensures a smooth, error-free verification process, helping providers gain approvals faster.
How Does Medical Credentialing Work?

Provider credentialing is a complex process that involves various steps. As a candidate, you should have information on the whole process to understand the importance of the documents you will provide to the credentialing committee. Important steps are below:
- The committee gathers all the information and credentials from the candidate and asks the candidate to apply with accurate data.
- Then, all credentials are verified from the primary source. A primary source is the actual institute that has issued the credential.
- After every verification, a background check is done, and red flags are determined if any.
- A final decision is made by the committee, and privileges are granted to the approved healthcare professional.
Why Physician Credentialing is Critical
Physician credentialing verifies and evaluates the qualifications, training experience and professional background of medical practitioners and healthcare providers. Healthcare professionals need credentialing to fulfill essential regulatory conditions for medical practice. The process confirms the competency and qualifications of healthcare providers. The process leads to better patient safety standards while ensuring treatment quality. Credentialing enables healthcare providers to meet state and federal regulations, which helps prevent legal problems.
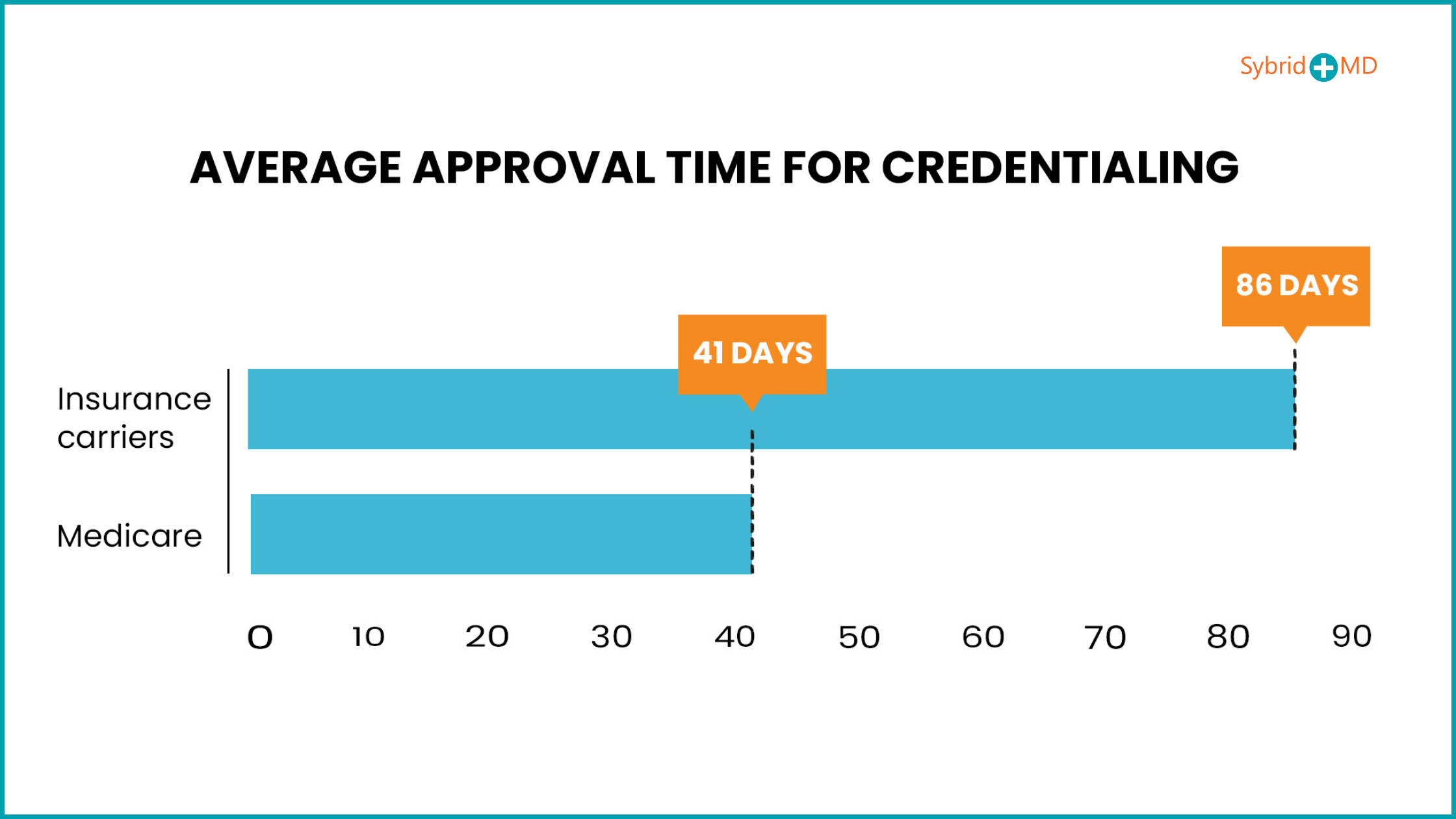
It minimizes the risks of legal repercussions. The turnaround time for credentialing in medical billing differs due to multiple influencing factors. The provider enrollment, chain, and ownership system (PECOS) is a feature of government programs like Medicare. Medical billing provider enrolment and credentialing processes are completed more quickly than those of commercial insurance providers since Medicare takes an average of 41 days to approve. The processing time for commercial insurance carriers to complete the necessary procedures ranges from 60 to 180 days.
Furthermore, credentialing aids in risk management. Healthcare facilities can lower their vulnerabilities when they keep their credentials current. Institutional stability and security levels rise as a result of these measures.
Key Components Of The Physician Credentialing Checklist – Preparation Guide
The following components of this process are mentioned in the checklist:
- Personal identification
- Educational background
- Professional licensure and certifications
- Work history and experience
- Professional liability insurance
- Continuing education
- Peer references
- Immunization and health records
- Background checks
1. Personal Identification
The first part is getting the provider’s personal information to get insight into his contact, location, and other information. Government-issued IDs, such as passports or driving licenses, are asked to be submitted. A social security number (SSN) is asked for background checks and verification. You need to add the things in the following order in the application form:
- First and last name
- Email address
- Street address
- Phone number
- Driver’s license
- Social Security card
2. Educational Background
Educational background is checked to verify the legitimacy of the educational degrees like diplomas, training, and residency. This helps the committee to know whether the candidate has completed his medical study or is not required to train and practice medicine in a healthcare organization. There are the following documents which are mentioned in the physician credentialing checklist.
- Diplomas
- Transcript
- Residency and fellowship certificates
3. Professional Licensure And Certifications
Collecting licensure is the most hectic and time-consuming event in the whole process. As doctors deal with the lives of patients, it is necessary to check the eligibility of physicians for practicing medicine and prescribing drugs. Licensure is provided by the relevant boards and regulatory bodies to allow healthcare providers to practice in specified states.
- Copies of all current state medical licenses and wall certificates
- Copy of current Federal DEA and State Controlled Substance Registrations or certificates
- Copies of BLS, ACLS, ATLS, PALS, APLS, and NRP certificates
- ACLS/BLS certification
- ECFMG certificate number and info on Fifth Pathway
- Copy of NBME, USMLE, FLEX, or SPEX scores
4. Work History And Experience
If the healthcare provider has previous work experience and has worked for other organizations, then it is recommended to check the background. It helps to find out the professional behavior and attitude of the physician. Documents required are:
- Curriculum vitae (CV): A detailed, well-organized CV showing the details of work history. Assigned position, given privileges, duration of employment, and responsibilities are mentioned in the work history detail.
- Work History Verification: A verification certificate issued by the previous employer is needed to verify the accuracy of the mentioned information in the application form.
- Explanation of Gaps: If a healthcare provider has remained off from work for some time then, he is responsible for presenting the document explaining the reason behind gaps.
5. Professional Liability Insurance
To protect patients and healthcare organizations from negligent and non-professional healthcare practitioners, it is recommended that malpractice claims be checked. If any, the application should be rejected at once. Therefore, it is advised that all candidates get professional liability insurance to protect themselves and the institute from malpractice claims and severe penalties. Professional liability insurance is provided to providers with a clean background without any malpractice or ethical problems.
Nothing is certain, and any mishap can happen at the hands of the provider. In this case, insurance companies handle the claims. The provider and hospital can escape the penalty charges. So, the Credentialing Committee only approves those people with liability insurance, which means they do not have any tarnished background. Also, their future claims will be handled by insurance companies.
6. Continuing Education
The medical field is ever Medi-evolving, and many new techniques and treatment methods are introduced into the market. Therefore, physicians must keep track of new updates. CME (continuous medical education) is designed with various workshops, seminars, lectures, and skill labs to present education to healthcare providers.
During credentialing, at least track of the last 3 years of CME is asked and evaluated to check the professional attitude and dedication of providers towards the welfare of patients. The credentialing committee asks for the current CME status and CME completed projects. Documents like CME certificates and CME logs are needed for credentialing.
CME certificates denote the completed CME activities, while the CME log gives information about the date, topics, and duration of the course taken. The CME log also shows the total credits earned by healthcare practitioners.
7. Peer References
Ethical behavior and professional conduct hold the same importance as educational skills in practicing medicine and taking care of patients. Therefore, while recruiting new healthcare providers, the credentialing committee demands references and feedback from the provider’s colleagues and previous employers.
A letter of recommendation (LOR) attesting to the provider’s character and professionalism should be presented to the committee, signed, and verified by colleagues and supervisors. The credentialing body also gives the candidate a peer reference form. The candidate is supposed to submit the completed form. The credentialing committee can verify the information by contacting previous colleagues and employers.
8. Immunization And Health Records
Hospitals are not safe places for anyone, including doctors and patients. Both parties are at high risk of infection and multiple diseases. Healthcare providers are continuously dealing with patients and are in direct contact with them. That’s why it is crucial to check the health status of providers. The following documents are needed:
- An immunization certificate shows that the vaccination history is up to standard.
- Complete medical report
- Recent TB test results
9. Background Check
A background check is necessary to ensure that the healthcare provider is not involved in any type of illegal activity and that he does not have any suspicious track record. The following documents are required:
- Criminal background check report
- National Practitioner Data Bank (NADB) reports to check the malpractice payment or any other adverse actions.
- The OIG exclusion list is to confirm that the provider is not excluded from participating in federal plans.
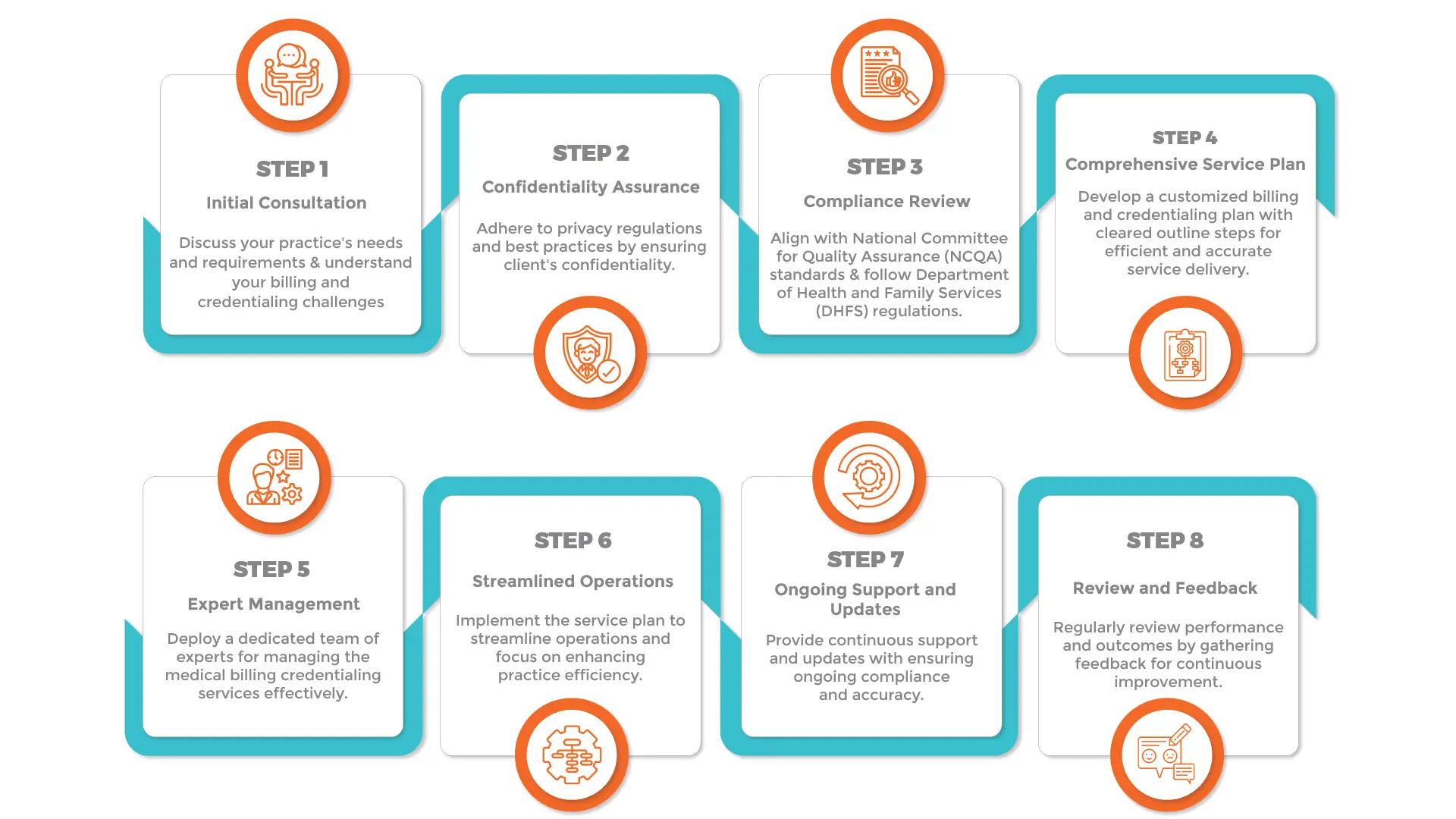
Step-by-Step Physician Credentialing Process – Application & Verification Guide
It is hard to figure out the exact answer for what are the steps to credentialing. Physician credentialing isn’t something that happens overnight. The credentialing process extends over weeks due to the requirement to verify information from various sources. Here’s a brief overview of the steps involved:
1. Initial Preparation
Collect all required documents and information about the healthcare provider before initiating the credentialing process. This includes:
- Education and Training: The educational background of healthcare providers, including degrees and certifications, along with their training programs.
- Work History: Work History includes details about previous employment positions and current job roles.
- Licenses: Required documentation includes state medical licenses and board certifications.
- Malpractice Insurance: Malpractice Insurance: Documentation that shows active malpractice insurance coverage.
- Hospital Privileges: Hospital Privileges encompass documented affiliations with hospitals along with granted privileges.
- References: Professional references obtained from work colleagues or supervisory staff
2. Submitting the Credentialing Application
After collecting all necessary information, the provider needs to send a credentialing application to the insurance company. The credentialing application needs to demonstrate the provider’s qualifications alongside their capacity to treat patients.
3. Primary Source Verification
The credentialing expert makes sure the physician’s submitted information is both accurate and authentic. The insurance company undertakes primary source verification once the application has been submitted. This involves verifying the provider’s:
- Education and degrees.
- Training and residency programs.
- Licenses and certifications.
- Work history and current employment status
4. Background Checks
A complete background investigation is performed on the physician. The background check process includes criminal background investigations and checks for any disciplinary actions or malpractice claims, along with any measures taken against the physician’s medical license.
5. Peer References
The physician submits professional references from their colleagues, supervisors, or healthcare partners to confirm their competence and professionalism. The credentialing specialist reaches out to the physician’s provided references to collect information about their clinical abilities and professional behavior and overall job performance.
6. Credentialing Review
The credentialing and compliance teams review physicians’ qualifications and training to verify adherence to organizational standards.
7. Decision and Notification
The review process leads to a decision about the physician’s application. The physician receives notification about the decision which might be approval or denial or a requirement for additional information.
8. Recredentialing
Physicians who receive approval undergo regular credential reviews to verify their qualifications remain aligned with organizational standards. The re-credentialing process takes place at standard periods which may range from once a year to every two years according to an organization’s specific guidelines.
Fast-Track Your Credentialing Process – Speak with Our Experts Now!
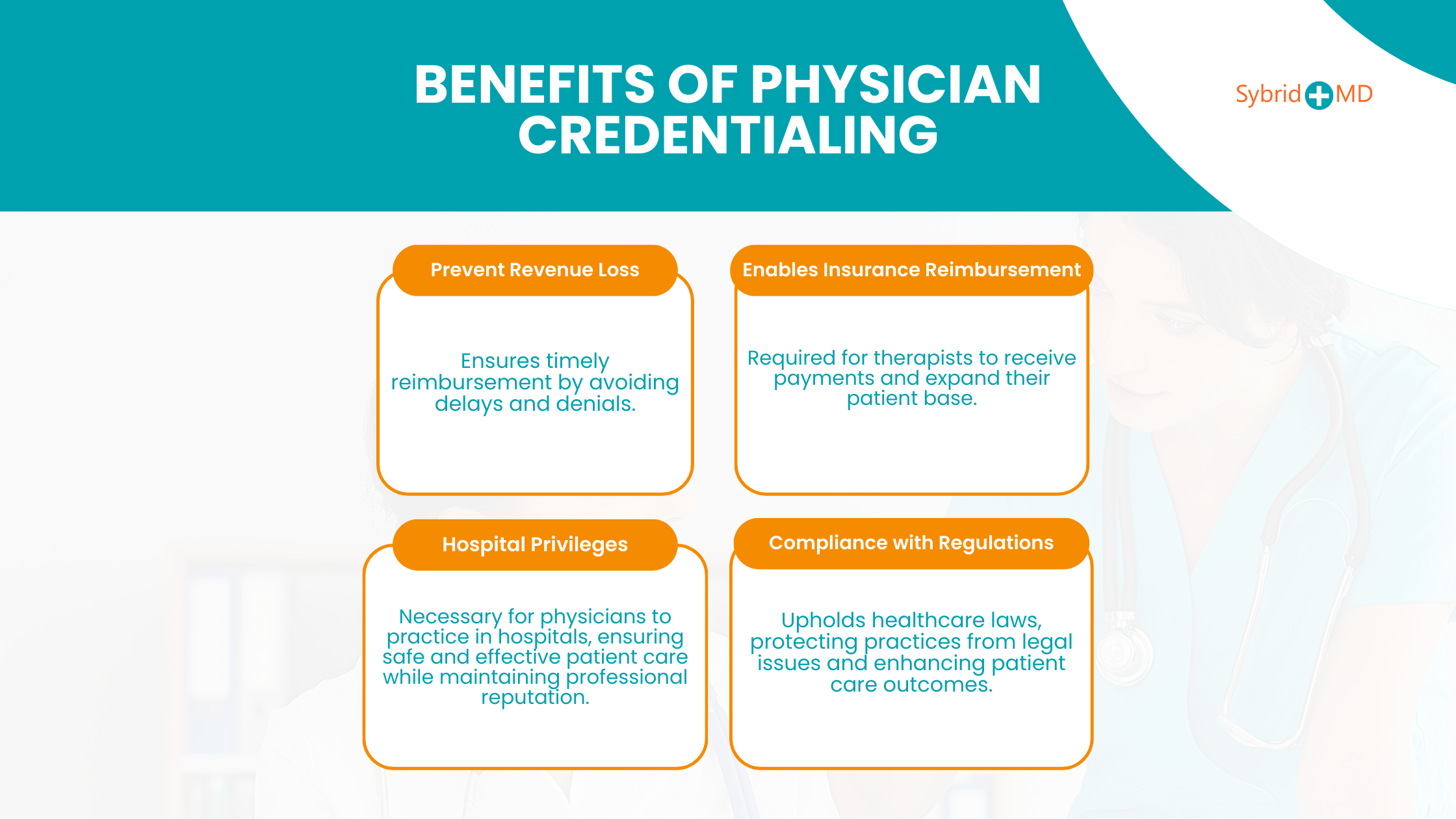
Benefits of Physician Credentialing
Some of the advantages of medical credentialing are as follows:
Benefits of Physician Credentialing
1. Prevent losing revenues
Proper credentialing helps medical practices maintain revenue by avoiding reimbursement delays and denials. Healthcare practices that don’t obtain proper credentialing face financial losses from delayed or denied reimbursements.
2. Enables Insurance Reimbursement
Insurance companies require therapists to have proper credentials before they can receive payment for physical therapy services. Medical practices that fail to obtain proper credentialing will not be able to submit insurance claims and face the risk of substantial revenue decline. Credentialing permits therapists to receive insurance payments while expanding their patient pool and treating those with insurance coverage. The financial sustainability of practices that depend on insured clients depends heavily on this essential financial support system.
3. Compliance with Regulations
Medical credentialing for therapists and clinics requires strict compliance with regulations as a primary requirement. The credentialing process upholds healthcare laws at both state and federal levels to protect practices from legal issues and financial consequences. Therapists who adhere to proper credentialing measures protect their practice from risks associated with non-compliance, which safeguards their professional reputation and financial stability. The commitment to regulations results in better patient care outcomes.
4. Hospital privilege
Healthcare facilities and hospitals mandate physicians to pass through credentialing procedures before they receive permission to practice at these institutions. The process of credentialing makes certain that physicians fulfill hospital standards to deliver both safe and effective patient care. Physicians need to go through credentialing to gain permission to admit patients and conduct medical procedures as well as obtain access to hospital resources.
The credentialing process establishes and sustains a physician’s professional reputation by verifying their qualifications and conducting background checks for potential issues.
Addressing Common Credentialing Challenges
Credentialing remains a crucial and complicated component of healthcare because failures in its management can cause extensive delays and financial issues along with considerable frustration.
1. Keeping up-to-date with Info
Medical organizations struggle to collect essential data from applicants during credentialing. The majority of submitted applications contain errors because they include faulty information or missing details. Applications require re-verification for even minimal updates, including changes to residence or contact details through the CAQH system.
The healthcare credentialing process becomes more complex and time-consuming when information in applications is missing or inaccurate. The issue intensifies when you consider the high frequency at which healthcare professionals move between different organizations where they work. Healthcare organizations need to continually update their records to prevent complications during the credentialing process.
2. Time-Consuming
The healthcare credentialing process requires a lot of time. An application review process will not exceed 90 days. When contract negotiators and health insurers participate in the procedure, it can stretch up to 6 months. Because this process takes so much time most healthcare organizations must stop their regular operations during this period.
3. Ensuring Compliance
The credentialing procedure presents the most significant compliance difficulties as mentioned earlier. Each state imposes specific laws and guidelines which providers must follow. National organizations like CAQH enforce their own regulations which providers need to adhere to. This situation leads to operational difficulties because healthcare credentialing rules vary from state to state. Healthcare rules and policies change frequently and lack predictability. Working with complex and evolving rules requires the assistance of a reliable credentialing service provider or system.
4. Protecting the Private info of Healthcare Providers
The credentialing procedure requires background checks as a mandatory step. The verification of a candidate’s skills and credentials to provide patient care requires these checks. The application process demands the submission of essential documents, including practicing licenses and educational credentials, among others, which makes privacy protection vital. The certification body needs to obtain the complete background information from the applicant. If applicants do not submit essential information, their physician applications will be rejected. A healthcare credentialing system will help you store all updated data securely and shield it from unauthorized views. The majority of organizations currently do not possess adequate platforms needed to secure crucial data.
Avoid Delays & Errors – Get Professional Credentialing Assistance Now!
Practical Solutions for Overcoming Credentialing Challenges
The primary difficulty during credentialing procedures involves the collection and validation of required documentation. If providers neglect any minor detail in this procedure, they risk losing specific job opportunities or hospitals may encounter accreditation denials. The initial measure for minimizing this task requires streamlining the documentation process.
1. Streamlining Documentation:
Credentialing administrative burdens are reduced greatly when documentation processes undergo streamlining since this represents the initial step. Maintaining flawless records while making certain that all necessary details are accessible defines this process. Checklists and templates provide a valuable means to guarantee all applications satisfy requirements and maintain thoroughness. A proactive strategy reduces the risk of process delays due to missing or incorrect information, allowing for an uninterrupted workflow.
2. Maintain careful awareness of each state’s individual regulations
Researching healthcare system regulations, as well as related laws and guidelines, is essential. Because each state has various standards, you will need the assistance of healthcare credentialing specialists who are knowledgeable of rules and can assist you with a smooth compliance transition. Checking your state’s regulations for:
- Licenses
- Certifications
- Education qualifications.
- Expert Assistance
Navigating the complex requirements of credentialing demands time and resources which makes expert assistance a highly effective solution. The workload of internal staff diminishes when organizations hire credentialing specialists or outsource to professional credentialing services. Professionals who understand credentialing requirements can handle the process more effectively. NCDS Medical Billing provides comprehensive credentialing support which enables providers to handle all necessary steps from application submission to continuous compliance so healthcare professionals can dedicate their time to patient care instead of administrative work.
Role of Technology in Credentialing
Medical credentialing becomes easier through multiple technological methods. We will explore the ways in which technology facilitates the completion of this process in a smooth and efficient manner.
1. Electronic Applications
The credentialing process has become more efficient with the use of electronic applications technology. Healthcare providers who submit their credentials electronically benefit from time savings and reduced error rates. The processing of electronic applications moves at a quicker pace, which results in faster credentialing for healthcare providers.
2. Automated Verification
Technology accelerates the medical credentialing process with automated primary source verification. Credentialing organizations now have access to technology that allows them to verify healthcare provider credentials automatically by retrieving information from primary source databases like medical schools and state medical boards. The system removes the necessity for manual checks, which often consume time and introduce errors.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Medical credentialing processes benefit from the application of artificial intelligence (AI). AI algorithms process vast amounts of data to detect patterns and irregularities which might reveal problems with healthcare provider credentials. AI algorithms have the ability to evaluate malpractice history to detect behavior patterns that signify an increased risk of malpractice.
4. Digital Credentialing
The medical credentialing process utilizes digital credentialing technology to make operations more efficient. Digital credentialing means generating electronic credentials like digital badges or certificates that can be easily shared and verified online. Digital credentials offer enhanced security and efficiency compared to paper credentials while allowing for fast and straightforward verification.
Credentialing Lead Generation Checklist:
- Identify Your Target Audience: Determine Your Target Audience by Learning about the Essential Qualifications and Certifications Your Best Leads Need.
- Create an Engaging Landing Page: Design your landing page to showcase credentialing benefits alongside downloadable materials including this checklist.
- Offer a Free Resource: Make a free resource available, such as an e-book or credentialing guide to obtain contact information from users.
- Implement SEO Strategies: Implement powerful SEO tactics by integrating precise keywords to increase search engine traffic to your site.
- Leverage Social Media: Use LinkedIn and Twitter alongside other industry-specific channels to market your lead magnet.
- Set Up Automated Email Sequences: Automate email sequences to engage leads with valuable information and compelling calls to action, which follow them automatically.
- Track Metrics: Measure open rates and conversion rates along with engagement levels to refine lead generation strategies.
Conclusion – Physician Credentialing Checklist
Physician credentialing is a critical process that ensures healthcare providers meet industry standards, maintain compliance, and secure timely insurance reimbursements. A structured credentialing checklist helps avoid errors, delays, and compliance risks.
To streamline credentialing, providers should prepare:
- Personal identification & educational background
- State medical licenses, board certifications & peer references
- Work history, malpractice insurance, and compliance records
Healthcare organizations often face credentialing delays due to missing documents, outdated information, or inefficient verification. Leveraging credentialing automation tools and expert services can reduce administrative burdens and speed up approvals.
A well-organized physician credentialing checklist ensures faster approvals, regulatory compliance, and an efficient onboarding process for new providers. Ensuring accuracy and consistency in credentialing procedures is essential for maintaining the quality and integrity of patient care.
Subscribe for More Tips on Physician Credentialing & Compliance!
FAQs
What is a physician credentialing?
Physician credentialing involves validating and evaluating physicians’ qualifications alongside their training history professional experience, and background. Healthcare professionals need to complete this essential step to satisfy medical practice regulations.
What are the credentialing requirements?
This includes primary source verification of various aspects, including:
- Education and training. Licensure. The verification process covers the physician’s active medical license status and any limitations or disciplinary actions attached to it.
- Board certification.
- Work history.
- Hospital privileges.
- Quality measures.
What is checked during a credentialing process?
During the credentialing process, the following are typically checked:
The credentialing process checks degrees along with certifications and specialized training within Education and Training.
- Licensure: Validity of professional licenses.
- Professional Experience: A record of past employment and relevant work experience.
- Criminal Background: Checking for criminal history.
- Malpractice and Legal History involves examining all previous malpractice claims and legal matters.
- References: Professional references and reputation.
- In certain professions, safety standards require drug and alcohol testing.
- The Sanctions/Exclusions section requires verification of disciplinary actions and exclusions imposed by regulatory bodies.
- Continuing Education involves maintaining professional growth while adhering to current industry standards.
What are the three types of credentialing?
The three types of credentialing are:
- Individual Credentialing focuses on checking the professional qualifications of specific individuals like healthcare providers or teachers.
- Organizational Credentialing assesses whether organizations meet industry standards through qualification evaluations (e.g., hospitals and schools).
- Supplier credentialing requires checking both qualifications and compliance standards for vendors and service providers, including suppliers and contractors.
What is the most restrictive type of professional credentialing?
The most restrictive type of professional credentialing is licensure, as it is legally required to practice in a specific profession and is regulated by government authorities.